(English follows)
Sono tante le grandi donne italiane che hanno lasciato il segno nella storia italiana e mondiale. Donne che hanno visto oltre i confini e i limiti imposti loro dalla società del tempo. Spinte da ambizione, pazienza, coraggio, lacrime e la forza di essere donna. Restano ancora oggi delle icone di intraprendenza a cui guardare per trovare ispirazione. Hanno sfidato le convenzioni, stabilito primati e modificato per sempre l’immagine della donna nel nostro paese diventando punti di riferimento per tutte noi nella storia, nell’arte, nella politica, nella scienza, nella letteratura e in molti altri ambiti. Un paragrafetto non basta per narrare la grandezza di queste 26 donne e di tantissime altre che, per mancanza di spazio, non sono incluse qui. Spero che questo sia uno spunto per approfondirne la conoscenza, e per ispirarti a continuare il lavoro iniziato da loro.
Sibilla Aleramo
Tina Anselmi
Augusta Bassi
Cristina Trivulzio di Belgiojoso
Milla Baldo Ceolin
Samantha Cristoforetti
Grazia Deledda
Christine de Pizan
Matilde di Canossa
Oriana Fallaci
Artemisia Gentileschi
Margherita Hack
Nilde Iotti
Anna Magnani
Alda Merini
Mina
Tina Modotti
Rita Levi Montalcini
Maria Montessori
Fernanda Pivano
Miuccia Prada
Teresa Sarti – Strada
Matilde Serao
Franca Viola
Monica Vitti
Lina Wertmüller
Sibilla Aleramo
Sibilla Aleramo, nata ad Alessandria nel 1876, è lo pseudonimo di Marta Felicina Faccio. E’ stata una scrittrice e poetessa femminista italiana meglio conosciuta per le sue rappresentazioni autobiografiche della vita di una donna nell’Italia della fine del XIX secolo. Si è distinta non solo per il suo talento in campo giornalistico e di scrittura, ma per una scelta di vita: prendere la decisione di abbandonare un marito violento e coltivare i propri talenti dedicandosi al lavoro. Il suo romanzo capolavoro intitolato “Una Donna”, racconta il proprio percorso di rinascita.
Tina Anselmi
Tina Anselmi, nata a Castelfranco Veneto nel 1927, è stata una importante politica e partigiana italiana e la prima donna ad aver ricoperto la carica di ministro della Repubblica Italiana.
E’ nota soprattutto per essere stata la principale proponente delle leggi italiane sulle pari opportunità, per cui si è sempre battuta nella sua vita politica. Infatti, nel 1977, ha approvato un disegno di legge che riconosceva i padri come tutori primari dei propri figli e consentiva sia ai padri che alle madri di avere del tempo libero per i propri figli. Nello stesso anno è stata varata un’importante legge sulla parità di genere nelle condizioni di lavoro, di cui Anselmi fu una sostenitrice fondamentale. Ha presieduto la Commissione Nazionale Pari Opportunità fino al 1994. Il suo ruolo è stato significativo nell’introduzione del Servizio Sanitario Nazionale in Italia.
Augusta Bassi
Augusta Bassi, nata a Milano nel 1926, è stata uno dei principali e più agguerriti avvocati per la difesa dei diritti delle donne. Celebre per aver difeso i diritti di Donatella Colasanti contro Angelo Izzo nel processo sul Massacro del Circeo. Si è distinta per la sua posizione fin dai primi anni Settanta in modo particolare per la tutela di Fiorella, una 18enne vittima di stupro. Questo è stato il primo Processo per stupro ad essere filmato e mandato in onda dalla RAI. In linea con il suo impegno per le cause femminili è stata una delle socie fondatrici del Telefono Rosa.
Cristina Trivulzio di Belgiojoso
Cristina Trivulzio di Belgiojoso, nata a Milano nel 1808, è stata una nobildonna e scrittrice italiana che ha partecipato attivamente al Risorgimento italiano, entrando in contatti con tutti i maggiori protagonisti dell’epoca, tra cui Carlo Alberto e con Napoleone III. Si e’ separata molto presto dal marito Belgiojoso con il quale ha avuto una figlia. Ha sovvenzionato insurrezioni, organizzato un battaglione a Napoli per contribuire alle Cinque Giornate di Milano, ha diretto gli ospedali a Roma durante gli scontri del 1849. A Parigi ha tenuto salotti con ospiti illustri e si è avventurata da sola in Oriente organizzando una comunità agricola partendo dal nulla. Tornata a Locate nel 1855 ha costruito asili, scuole e modernizzato il paese, portandolo ad un livello sociale molto al di sopra della situazione tipica di quel periodo.
Milla Baldo Ceolin
Milla Baldo Ceolin, nata a Legnano nel 1924, chiamata la signora del neutrino, è stata una fisica italiana e tra le protagoniste che hanno dato il maggior contributo allo sviluppo della fisica del XX secolo. E’ stata la prima professoressa a salire in cattedra all’Università di Padova. La sua ricerca si è concentrata su particelle elementari e interazioni deboli. In particolare tra le sue scoperte è quella sui mesoni K. E’ stata direttrice dell’Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) di Padova e ha diretto per cinque anni l’Istituto di Fisica “Galileo Galilei”. Ha lavorato alle macchine acceleratrici del CERN e anche negli Stati Uniti, in Russia e in Francia. Il 21 maggio 2008 è diventata socio dell’Accademia delle scienze di Torino.
Samantha Cristoforetti
Samantha Cristoforetti, nata a Milano nel 1977, è un’aviatrice, ingegnere, astronauta militare italiana, e la prima donna italiana negli equipaggi dell’Agenzia Spaziale Europea. Ha conseguito il record europeo e il record femminile di permanenza nello spazio in un singolo volo, 199 giorni, con la missione ISS Expedition 42/Expedition 43 Futura del 2014-2015.
Cristoforetti ha comandato la missione NEEMO 23 nel 2019 per testare tecnologie e obiettivi per missioni nello spazio profondo ed esplorazioni lunari sul fondo del mare. Il 21 luglio 2022 la Cristoforetti ha completato la sua prima passeggiata spaziale, durata 7 ore e 5 minuti.
Grazia Deledda
Grazia Deledda, nata a Nuoro nel 1871, è stata la prima donna italiana a vincere nel 1926 il Premio Nobel per la letteratura. Scrittrice di romanzi e opere teatrali, è ricordata per la sua non convenzionalità e potenza espressiva. Le sue opere traggono ispirazione dalle sue storie personali che trattano con profondità e con calore di problemi di generale interesse umano, quali il dolore e la morte, ed anche delle tradizioni patriarcali della società sarda.
Christine de Pizan
Christine de Pizan, o anche Cristina da Pizzano, nata a Venezia nel 1364, è riconosciuta come la prima scrittrice e poetessa di professione nel Medioevo apprezzata in tutta Europa. Ha vissuto in Francia alla corte di Carlo V. Con le sue opere è riuscita a soli 25 anni, rimasta vedova e senza padre, a provvedere al benessere economico della propria famiglia. «Dovetti diventare un uomo», scriveva riferendosi al suo compito di sostenere i tre figli e la madre. E’ diventata famosa per la rivendicazione del sapere e della dignità femminile. Le sue opere liriche e narrative traevano spunto dalla propria esperienza di vita, e non dalla tradizione religiosa o mitologica, come era frequente al tempo. Ha dato inizio alla cosiddetta Querelle des femmes (“Querela delle donne”) dopo avere letto due opere rispettivamente di Boccaccio e di Jean de Meun, i quali consideravano la donna un essere vizioso per natura. Nell’opera intitolata Livre de la Cité des Dames (“Libro della Città delle Dame”), elencava esempi di donne virtuose e importanti nella storia dell’umanità.
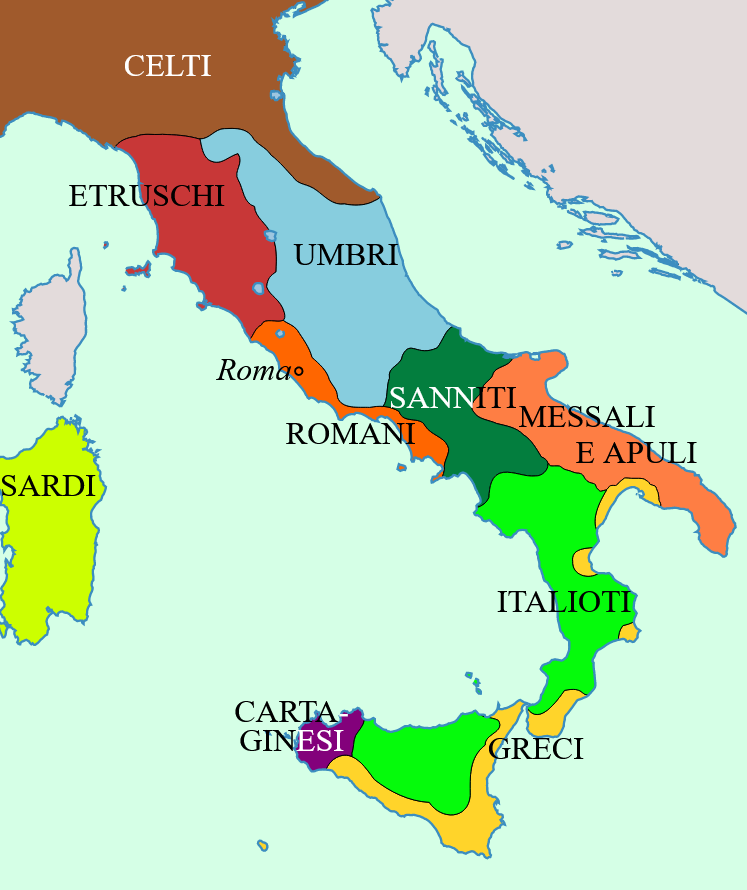
Matilde di Canossa
Matilde di Canossa, nata forse a Mantova nel 1046, è stata una delle poche donne che hanno avuto nella storia italiana un ruolo tanto importante. Ha retto per quarant’anni uno Stato che si estendeva su buona parte dell’Italia settentrionale e centrale, e ha partecipato da protagonista alla lotta tra l’Impero e la Chiesa. E’ diventata un’assidua sostenitrice del Papato dopo essere stata fatta prigioniera dall’imperatore Enrico III, insieme alla madre, un’esperienza che l’ha molto impressionata. Si è separata da Goffredo il Gobbo, al quale era stata data in sposa, dopo soli tre anni. Quando nel 1076 ha preso pieno possesso dei domini del padre, è diventata la più importante alleata di Papa Gregorio VII, che era fermamente intenzionato a dichiarare la superiorità del potere divino su tutti i poteri terreni, compreso l’Impero. E’ entrata nella storia e nella leggenda come nessuna donna prima di lei. Oggi riposa nella tomba scolpita dal Bernini ed è detta “onore e gloria d’Italia”.
Artemisa Gentileschi
Artemisia Gentileschi, nata nel 1593 a Roma, è stata una delle prime pittrici italiane riuscite a imporre il proprio talento in una società chiusa in cui le donne non avevano possibilità di emergere. Suo padre, un artista di origini toscane amico del pittore Caravaggio, ha incoraggiato il suo talento artistico. L’arte di Artemisia era originale, nonostante l’influenza caravaggesca, con capolavori di grande realismo nel complesso e fervente panorama artistico della Roma di inizio ‘600. La sua storia è anche legata al processo di stupro di cui era vittima, e che ha avuto il coraggio di denunciare. Artemisia ha sfidato le convenzioni del suo tempo ed è oggi ricordata come un’artista di primo piano nella storia dell’arte italiana.
Oriana Fallaci
Oriana Fallaci, nata a Firenze nel 1929 era una giornalista e scrittrice tra le più controverse del XX secolo. Sin da giovanissima, il clima di oppressione in cui è cresciuta l’ha spinta a prendere parte alla Resistenza come staffetta partigiana antifascista. La sua vocazione per il giornalismo è stata precoce e si coniugava all’attivismo politico. E’ diventata famosa per le sue indagini e i suoi reportage nel suo stile frontale e diretto, come quello relativo alla guerra del Vietnam nel 1967. Riusciva come poche figure della nostra cultura intellettuale a mettere in disaccordo le parti. Il suo è stato un ruolo da protagonista in una società dominata principalmente da figure maschili.
Margherita Hack
Margherita Hack, nata a Firenze nel 1922, conosciuta con il soprannome di “signora delle stelle”, è stata un’astrofisica e divulgatrice scientifica italiana. E’ stata professore ordinario di astronomia all’Università di Trieste, e membro delle più prestigiose società fisiche e astronomiche tra cui l’ESA e la NASA. Ha scoperto Epsilon Aurigae, una supergigante lontana 6500 anni luce e duecentomila volte più luminosa del sole. Nel 1994 ha ricevuto la Targa Giuseppe Piazzi per la ricerca scientifica e nel 1995 ha ricevuto il Premio Internazionale Cortina Ulisse per la divulgazione scientifica.
Si è distinta anche nella lotta per i diritti civili anche nella protezione degli animali.
Nilde Iotti
Leonilde Iotti, detta Nilde, nata a Reggio nell’Emilia nel 1920, è stata una politica italiana, prima donna eletta Presidente della Camera dei deputati per tre legislature, tra il 1979 e il 1992, per ben 12 anni e 307 giorni diventando la presidente della Camera rimasta in carica più a lungo in assoluto nella storia della Repubblica Italiana.
E’ stata una figura politica fondamentale nell’Italia del dopoguerra e nella neonata Repubblica. Come partigiana e comunista si è impegnata attivamente in numerose battaglie etiche e sociali.
Era una riformista con il Vangelo della Costituzione sempre in mano e sosteneva che la democrazia deve rinnovarsi se vuole essere democrazia. Il suo pensiero si traduceva in azioni, lotte, proposte di riforme istituzionali.
Anna Magnani
Anna Magnani, nata a Roma nel 1908, è considerata una delle maggiori attrici femminili della storia e simbolo del cinema del neorealismo italiano dell’epoca. Era profondamente legata alla città di Roma ed è la donna a cui probabilmente più si lega la storia dello spettacolo in Italia. Sono celebri soprattutto le sue interpretazioni in film come “Roma città aperta”, “Bellissima”, “Mamma Roma” e “La rosa tatuata”, per cui ha vinto un Oscar nel 1956 come miglior attrice protagonista.
Grazie alla sua bravura e la sua fama è una delle poche attrici italiane che è riuscita a conquistare anche una stella sulla Walk of Fame di Hollywood.
Alda Merini
Alda Merini, nata a Milano nel 1931, è sicuramente la più grande poetessa italiana del 20esimo secolo. Già dall’età di 15 anni scriveva le sue poesie. Anche se viveva in una condizione di povertà a causa della guerra, lei perseguiva i suoi sogni. E’ nota per la profondità dei suoi componimenti che sono stati ispirati dalla sua vita travagliata. Infatti a causa di sofferenze mentali, dovuti anche a violenze coniugali, è stata internata in un ospedale psichiatrico. E’ qui che ha constatato la crudeltà di dottori e religiosi e ne è uscita con una grande consapevolezza sul dolore e sulla condizione umana.
Lei stessa scriveva “Dico spesso a tutti che quella croce senza giustizia che è stato il mio manicomio non ha fatto che rivelarmi la grande potenza della vita”. Le sue frasi sull’amore e sulla vita sono di ispirazione a tutte le donne.
Mina
Mina, pseudonimo di Mina Anna Maria Mazzini, nata a Busto Arsizio nel 1940, è senza dubbio la cantante italiana pop più famosa di sempre. È ricordata per la sua tecnica impeccabile e per la sua grande varietà interpretativa. Ha collaborato con vari autori e musicisti, tra cui Ennio Morricone, il quale ha creato per lei l’arrangiamento della canzone “Se telefonando”. Mina era un vero personaggio pubblico che è entrato nelle televisioni di tutti gli italiani, ma anche una donna anticonformista che ha fatto scandalo per le sue scelte di vita. Infatti è stata anche la prima donna italiana a indossare una minigonna in televisione.
Tina Modotti
Tina Modotti, nata a Udine nel 1896, è considerata una delle più grandi fotografe dell’inizio del XX secolo. I più importanti istituti e musei di tutto il mondo conservano le sue opere fotografiche.
Ha emigrato appena sedicenne dall’Italia agli Stati Uniti, dove ha vissuto una vita bohemienne grazie anche all’incontro di personaggi che vivevano l’arte a tutto tondo, come il fotografo Edward Weston, che è diventato il suo mentore. Si è innamorata della cultura messicana alla quale ha dedicato i propri scatti che includono persone e paesaggi fino al 1928 quando ha incontrato il fondatore del partito comunista cubano Julio Antonio Mella assassinato l’anno successivo. A causa delle sue idee politiche e per i suoi legami con il partito comunista la fotografa è stata esiliata e dal ’31 si è concentra totalmente sull’attivismo politico.
Rita Levi Montalcini
Rita Levi Montalcini, nata nel 1909 a Torino, è stata neurologa e senatrice a vita italiana. Suo padre era autoritario e disapprovava fortemente l’istruzione post-secondaria delle donne. A 20 anni Rita Levi aveva capito che non poteva assolutamente adattarsi a un ruolo femminile come concepito da suo padre e gli ha chiesto il permesso di studiare medicina. Essendo poco istruita, in soli otto mesi ha studiato i programmi completi di greco, latino e matematica ed è stata ammessa alla facoltà di medicina all’Università di Torino.
Ha iniziato la sua carriera scientifica in pericolo, come ebrea nell’Italia fascista per poi trionfare con le sue ricerche negli anni cinquanta sul sistema nervoso che l’hanno portata alla scoperta e all’identificazione del fattore di accrescimento della fibra nervosa o NGF, per la quale ha vinto il Nobel per la medicina 1986. Ha continuato il suo lavoro da ricercatrice fino all’età di 103 anni.
Maria Montessori
Maria Montessori, nata a Chiaravalle nel 1870, è stata una delle prime donne a ottenere una laurea in medicina in Italia. E’ conosciuta per il metodo educativo che porta il suo nome “Il Metodo Montessori”, adottato in tutto il mondo in migliaia di scuole materne, elementari e superiori. Il suo metodo pedagogico montessoriano si fonda sull’idea centrale secondo cui ciascun bambino possiede un potenziale psichico ed intellettivo unico ed irripetibile e che per questo, nel rispetto del proprio sviluppo, deve essere accompagnato nella crescita in modo da potersi esprimere liberamente. Ha viaggiato in vari paesi per diffondere la propria teoria educativa. In India ha vissuto anche un’esperienza di prigionia con il figlio durante la seconda guerra mondiale, in quanto cittadina di un paese nemico. Le scuole montessoriane vengono ancora oggi preferite ad altre.
Fernanda Pivano
Fernanda Pivano, detta Nanda, nata a Genova nel 1917, è stata una traduttrice e saggista italiana. Una figura di rilievo nel panorama culturale italiano per il suo impegno nella traduzione e divulgazione di opere della letteratura americana contemporanea, in particolare le opere della beat generation. Come saggista, ha confermato in Italia un metodo critico basato sulla testimonianza diretta, sulla storia del costume e sull’indagine storico-sociale degli scrittori e dei fenomeni letterari. Era una vivacissima animatrice della cultura, scopritrice di talenti. Una intellettuale indipendente in un periodo in cui i giovani intellettuali erano oppressi dal regime, dalla guerra, dalla povertà e da un isolamento che non era soltanto personale. Attraverso lo studio ha manifestato il modo in cui la donna italiana è potuta uscire dai ruoli mediocri imposti dall’epoca e dal fascismo.
Miuccia Prada
Miuccia Prada, nata a Milano nel 1949, è una stilista e imprenditrice italiana. Ha trasformato il marchio Prada, che ha ereditato nel 1978 dal nonno fondatore in un simbolo di eleganza e avanguardia conosciuto e ammirato in tutto il mondo. Ha iniziato a progettare accessori e ha firmato la prima linea di prêt-à-porter, imponendo a livello internazionale il marchio Prada come la griffe tra le più rappresentative del gusto minimalista. Il successo del marchio sono dovute alle sue intuizioni e alle sue collaborazioni. Ha ricevuto il dottorato onorario dal Royal college of art di Londra nel 2000 per la continua sperimentazione di materiali e l’originale innovazione estetica. Nel 2015 è stata insignita del titolo di Cavaliere di Gran Croce dell’Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana.
Teresa Sarti – Strada
Teresa Sarti, coniugata Strada, nata a Sesto San Giovanni nel 1946, è stata una filantropa e docente italiana, cofondatrice con il marito Gino Strada della ONG Emergency nel 1994, della quale è stata anche prima presidente. L’idea di creare un presidio medico in zone di guerra è proprio di Teresa. Inoltre era convinta che bisognava partire dalle scuole per creare una nuova coscienza e mettere le basi per un mondo migliore. Infatti ha prodotto per gli studenti un fumetto ad hoc, con protagonista il Lupo Alberto, molto amato da bambini e adolescenti. Il motto è: sopra la guerra c’è chi campa, sotto la guerra c’è chi crepa. E’ classificata tra le tredici donne che hanno fatto l’Italia.
Matilde Serao
Matilde Serao, nata a Patrasso nel 1856, è stata una scrittrice e giornalista. Una vera e propria icona nel campo del giornalismo, è stata la prima donna ad aver fondato e diretto un quotidiano, Il Mattino. Il mondo napoletano, così ricco di ispirazione e contraddizioni, nutriva la sua voglia di scrivere, raccontare, e parlare. Per lei il giornalismo era terreno di osservazioni, di costumi, che poi raccontava nei suoi romanzi.. Alle sue note sulla moda, sui cibi, lo sport, gli eventi mondani, le novità del progresso, gli usi e costumi faceva da contraltare un’attenzione particolare a fatti e avvenimenti sociali. Pubblicava articoli anche sul Giornale delle Donne, una delle principali riviste emancipazioniste del tempo.
Franca viola
Franca Viola, nata a Trapani nel 1947, è passata alla storia per essere stata la prima donna italiana ad aver rifiutato un matrimonio riparatore. A soli diciassette anni, ha avuto il coraggio di alzare la voce e rifiutare il matrimonio riparatore con l’uomo che l’aveva stuprata per otto giorni, riuscendo a denunciarlo e facendogli ottenere una condanna di 11 anni. All’epoca l’articolo 544 del codice penale prevedeva il “matrimonio riparatore”. Infatti la legge la imputava come “donna svergognata”. Secondo la condanna morale del tempo, la ragazza non essendo più vergine doveva sposare il suo stupratore per mantenere l’onore della famiglia, oppure sarebbe rimasta zitella per sempre. Franca e la sua famiglia pronunciarono un rivoluzionario “no”. Per la prima volta nella storia italiana una donna si è opposta alla legge degli uomini e ha cambiato per sempre il corso della giustizia nei casi di abuso. Se oggi la violenza sessuale è un reato punito dalla legge in Italia, il merito va a questa giovane donna fiera e coraggiosa.
Monica Vitti
Monica Vitti, pseudonimo di Maria Luisa Ceciarelli, nata a Roma nel 1931, è stata un’attrice italiana molto famosa nel mondo del cinema. Ha iniziato la sua carriera cinematografica negli anni ’50 in film diretti da registi come Michelangelo Antonioni, Federico Fellini e Mario Monicelli. E’ stata spesso associata alla “trilogia dell’incomunicabilità” di Antonioni, in cui ha interpretato il ruolo di donne inquiete e insoddisfatte, in cerca di un significato nella vita. Un’icona di stile per la sua bellezza e il suo senso di moda. La sua caratteristica voce roca e l’innato brio di attrice comica l’hanno accompagnata per quasi quarant’anni di carriera. Ha vinto numerosi premi per la sua carriera cinematografica. E’ stata anche attivista per i diritti degli animali.
Lina Wertmüller
Lina Wertmüller, nata a Roma nel 1928, è stata una regista, sceneggiatrice e scrittrice italiana. Ha iniziato la sua carriera collaborando con Federico Fellini come aiuto regista. È stata la prima donna in assoluto ad aver ricevuto una candidatura agli Oscar come migliore regista per il film “Pasqualino Settebellezze” nella cerimonia del 1977. Temi dei suoi film sono vizi e virtù degli uomini e delle donne, di ogni tempo. Mescolava la guerra sessuale e la politica di sinistra in film provocatori che lei definiva grotteschi e che sfidano il genere come “Mimì metallurgico ferito nell’onore”, “Travolti da un insolito destino nell’azzurro mare d’agosto” e “Pasqualino Settebellezze”, che l’hanno affermata come una delle registe più originali degli anni ’70. Nel 2020 le è stato assegnato il Premio Oscar onorario alla carriera.
English version
There are many great Italian women who have left their mark on Italian and world history. Women who have seen beyond the boundaries and limits imposed on them by the society of the time. Driven by ambition, patience, courage, tears and the strength of being a woman. Still today they are icons of resourcefulness to look up to for inspiration. They have challenged conventions, established records and forever changed the image of women in our country, becoming points of reference for all of us in history, art, politics, science, literature and many other fields. A paragraph is not enough to narrate the greatness of these 26 women and many others who, due to lack of space, are not included here. I hope this is a starting point to deepen their knowledge, and to inspire you to continue the work started by them.
Sibilla Aleramo
Sibilla Aleramo, born in Alessandria in 1876, is the pseudonym of Marta Felicina Faccio. She was an Italian feminist writer and poet best known for her autobiographical depictions of a woman’s life in late 19th-century Italy. She stood out not only for her talent in journalism and writing, but for a life choice: making the decision to abandon an abusive husband and cultivate her talents by dedicating herself to work. Her masterpiece novel entitled “A Woman”, tells of her own path of rebirth.
Tina Anselmi
Tina Anselmi, born in Castelfranco Veneto in 1927, was an important Italian politician and partisan and the first woman to have held the position of minister of the Italian Republic. She is known above all for having been the main proponent of Italian laws on equal opportunities, for which she has always fought in her political life. Indeed, in 1977, she passed a bill that recognized fathers as the primary guardians of their children and allowed both fathers and mothers to have time off for their children. In the same year, an important law on gender equality in working conditions was passed, of which Anselmi was a fundamental supporter. She chaired the National Commission for Equal Opportunities until 1994. Her role was significant in the introduction of the National Health Service in Italy.
Augusta Bassi
Augusta Bassi, born in Milan in 1926, was one of the main and most aggressive lawyers for the defense of women’s rights. She is famous for having defended the rights of Donatella Colasanti against Angelo Izzo in the trial on the Circeo massacre. She has stood out for her position since the early 1970s, especially for the protection of Fiorella, an 18-year-old rape victim. This was the first Rape Trial to be filmed and broadcast by RAI. In line with her commitment to women’s causes she was a founding member of Telefono Rosa.
Cristina Trivulzio of Belgiojoso
Cristina Trivulzio di Belgiojoso, born in Milan in 1808, was an Italian noblewoman and writer who actively participated in the Italian Risorgimento, coming into contact with all the major protagonists of the time, including Carlo Alberto and Napoleon III. She separated very early from her husband Belgiojoso with whom she had a daughter. She subsidized insurrections, organized a battalion in Naples to contribute to the Five Days of Milan, directed hospitals in Rome during the clashes of 1849. In Paris she held salons with illustrious guests and ventured alone in the East by organizing an agricultural community starting from nothing. She returned to Locate in 1855 and built kindergartens, schools and modernized the country, bringing it to a social level far above the typical situation of that period.
Milla Baldo Ceolin
Milla Baldo Ceolin, born in Legnano in 1924, called the lady of the neutrino, was an Italian physicist and one of the protagonists who made the greatest contribution to the development of 20th century physics. She was the first female professor to take the chair at the University of Padua. Her research has focused on elementary particles and weak interactions. In particular, among her discoveries is the one on mesons K. She was director of the National Institute of Nuclear Physics (INFN) in Padua and directed the “Galileo Galilei” Institute of Physics for five years. She worked on accelerator machines at CERN and also in the United States, Russia and France. On 21 May 2008 she became a member of the Turin Academy of Sciences.
Samantha Cristoforetti
Samantha Cristoforetti, born in Milan in 1977, is an Italian aviator, engineer, military astronaut, and the first Italian woman in the crews of the European Space Agency. She achieved the European record and the female record for staying in space in a single flight, 199 days, with the ISS Expedition 42 / Expedition 43 Futura mission of 2014-2015. Cristoforetti commanded the NEEMO 23 mission in 2019 to test technologies and targets for deep space missions and lunar seabed explorations. On July 21, 2022, Cristoforetti completed his first spacewalk, which lasted 7 hours and 5 minutes.
Grace Deledda
Grazia Deledda, born in Nuoro in 1871, was the first Italian woman to win the Nobel Prize for literature in 1926. She wrote novels and plays, and is remembered for her unconventionality and her expressive power. Her works draw inspiration from her personal stories which deal with issues of general human interest, such as pain and death, in a deep and warm manner, as well as with the patriarchal traditions of Sardinian society.
Christine de Pizan
Christine de Pizan, or even Cristina da Pizzano, born in Venice in 1364, is recognized as the first professional female writer and poet in the Middle Ages appreciated throughout Europe. She lived in France at the court of Charles V. With her works she managed at only 25 years old, left a widow and without a father, to provide for the economic well-being of her family. “I had to become a man,” she wrote, referring to her task of supporting her three children and her mother. She became famous for claiming female knowledge and female. Her lyrical and narrative works drew inspiration from her own life experience, and not from religious or mythological tradition, as was frequent in her time. She started the so-called Querelle des femmes (“Women’s lawsuit”) after reading two works respectively by Boccaccio and Jean de Meun, who considered women to be vicious by nature. In the work entitled Livre de la Cité des Dames (“Book of the City of Ladies”), she listed examples of virtuous and important women in the history of humanity.
Matilda di Canossa
Matilde di Canossa, perhaps born in Mantua in 1046, was one of the few women who played such an important role in Italian history. She ruled for forty years a State that extended over a large part of northern and central Italy, and participated as a protagonist in the struggle between the Empire and the Church. She became a staunch supporter of the Papacy after being taken prisoner by Emperor Henry III, along with her mother, an experience which greatly impressed her. She separated from Goffredo il Gobbo, to whom she was given in marriage, after only three years. When in 1076 she took full possession of her father’s domains, she became the most important ally of Pope Gregory VII, who was determined to declare the superiority of divine power over all earthly powers, including the Empire. She entered history and legend like no woman before her. Today she rests in the tomb sculpted by Bernini and is called the “honor and glory of Italy”.
Artemisa Gentileschi
Artemisia Gentileschi, born in 1593 in Rome, was one of the first Italian painters who managed to impose her talent in a closed society in which women had no chance to emerge. Her father, a Tuscan-born artist friend of the painter Caravaggio, encouraged her artistic talent. Artemisia’s art was original, despite the Caravaggio influence, with masterpieces of great realism in the complex and fervent artistic panorama of early 1600s Rome. Her story is also linked to the rape process of which she was a victim, and which she had the courage to denounce. Artemisia defied the conventions of her time and is remembered today as a leading artist in the history of Italian art.
Oriana Fallaci
Oriana Fallaci, born in Florence in 1929, was one of the most controversial journalists and writers of the 20th century. From a very young age, the climate of oppression in which she grew up prompted her to take part in the Resistance as an anti-fascist partisan relay. Her vocation for journalism was precocious and was combined with political activism. She became famous for her investigations and reports in her frontal and direct style, such as the one relating to the Vietnam War in 1967. She was able, like few figures in our intellectual culture, to put the parties at odds. Hers was a leading role in a society dominated mainly by male figures.
Margherita Hack
Margherita Hack, born in Florence in 1922, known by the nickname of “lady of the stars”, was an Italian astrophysicist and science popularizer. She was a fulltime professor of astronomy at the University of Trieste, and a member of the most prestigious physics and astronomy societies including ESA and NASA. She discovered Epsilon Aurigae, a supergiant 6,500 light years away and two hundred thousand times brighter than the sun. In 1994 she received the Targa Giuseppe Piazzi for scientific research and in 1995 she was granted the Cortina Ulisse International Prize for scientific dissemination. She has also distinguished herself in the fight for civil rights and in the protection of animals.
Nilde Iotti
Leonilde Iotti, known as Nilde, born in Reggio Emilia in 1920, was an Italian politician, the first woman elected President of the Chamber of Deputies for three legislatures, between 1979 and 1992, for 12 years and 307 days, becoming the president of the Chamber who remained in office for the longest time ever in the history of the Italian Republic.
She was a key political figure in post-war Italy and in the newly formed Republic. As a partisan and communist she actively engaged in numerous ethical and social battles. She was a reformist with the Gospel of the Constitution always in hand and maintained that democracy must renew itself if it wants to be democracy. Her thoughts translated into actions, struggles, proposals for institutional reforms.
Anna Magnani
Anna Magnani, born in Rome in 1908, is considered one of the greatest female actresses in history and a symbol of the Italian neorealist cinema of the time. She was deeply attached to the city of Rome and is probably the woman to whom the history of entertainment in Italy is most closely linked. Her most famous interpretations are in films such as “Rome, open city”, “Bellissima”, “Mamma Roma” and “The tattooed rose”, for which she won an Oscar in 1956 as best actress. Thanks to her acting skill and her fame, she is one of the few Italian actresses who has managed to also have a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame.
Alda Merini
Alda Merini, born in Milan in 1931, is certainly the greatest Italian poet of the 20th century. She wrote her poems from the age of 15. Even though she lived in poverty due to the war, she pursued her dreams. She’s known for the depth of her poems that were inspired by her troubled life. In fact, because of mental suffering, also due to conjugal violence, she was interned in a psychiatric hospital. It was here that she witnessed the cruelty of doctors and religious persons and she came away from it with a great awareness of pain and the human condition. She herself wrote “I often tell everyone that that cross without justice that was my asylum has only revealed to me the great power of life”. Her phrases about love and life are an inspiration to all women.
Mina
Mina, pseudonym of Mina Anna Maria Mazzini, born in Busto Arsizio in 1940, is undoubtedly the most famous Italian pop singer of all time. She is remembered for her impeccable technique and for her great variety of interpretations. She collaborated with various authors and musicians, including Ennio Morricone, who created for her the arrangement of the song “Se telefonando”. Mina was a real public figure who entered the televisions of all Italians, but also a nonconformist woman who caused a scandal for her life choices, in fact she was also the first Italian woman to wear a miniskirt on television.
Tina Modotti
Tina Modotti, born in Udine in 1896, is considered one of the greatest photographers of the early 20th century. The most important institutes and museums around the world preserve her photographic works. She emigrated from Italy to the United States at the age of sixteen, where she lived a bohemian life thanks also to meeting personalities who lived art all round, such as the photographer Edward Weston, who became her mentor. She fell in love with Mexican culture to which she dedicated her shots that include people and landscapes until 1928 when she met the founder of the Cuban communist party Julio Antonio Mella, assassinated the following year. Because of her political ideas and her ties to the communist party, the photographer was exiled and since 1931 she has totally concentrated on political activism.
Rita Levi Montalcini
Rita Levi Montalcini, born in 1909 in Turin, was a neurologist and Italian senator for life. Her father was authoritarian and strongly disapproved of women’s post-secondary education. At the age of 20, Rita Levi had understood that she absolutely could not adapt to a female role as conceived by her father and asked him for permission to study medicine. Being poorly educated, in just eight months she studied the full programs of Greek, Latin and mathematics and was admitted to the medical school at the University of Turin. She began her scientific career in danger, as a Jew in fascist Italy and then triumphed with her research on the nervous system in the 1950s which led her to the discovery and identification of the nerve fiber growth factor or NGF, for which she won the Nobel Prize for medicine in 1986. She continued her work as a researcher until the age of 103.
Mary Montessori
Maria Montessori, born in Chiaravalle in 1870, was one of the first women to obtain a medical degree in Italy. She is known for the educational method that bears her name “The Montessori Method”, adopted worldwide in thousands of kindergartens, elementary and high schools. Her Montessori pedagogical method is based on the central idea according to which each child possesses a unique and unrepeatable psychic and intellectual potential and that for this reason, in respect of their own development, they must be accompanied in their growth in order to be able to express themselves freely. She traveled to various countries to spread her educational theory. In India she also lived an experience of imprisonment with her son during the Second World War, as a citizen of an enemy country. Montessori schools are still preferred to others today.
Fernanda Pivano
Fernanda Pivano, known as Nanda, born in Genoa in 1917, was an Italian translator and essayist. She was an important figure in the Italian cultural panorama for her commitment in the translation and dissemination of works of contemporary American literature, in particular the works of the beat generation. As an essayist, she confirmed in Italy a critical method based on direct testimony, on the history of customs and on the historical-social investigation of writers and literary phenomena. She was a very lively promoter of culture, discoverer of talents. She was an independent intellectual at a time when young intellectuals were oppressed by the regime, by war, by poverty and by an isolation that was not only personal. Through her studies she demonstrated the way in which the Italian woman was able to emerge from the mediocre roles imposed by the time and by fascism.
Miuccia Prada
Miuccia Prada, born in Milan in 1949, is an Italian fashion designer and entrepreneur. She transformed the Prada brand, which she inherited in 1978 from her founding grandfather, into a symbol of elegance and avant-garde, renowned and admired all over the world. She started designing accessories and signed the first prêt-à-porter line, establishing the Prada brand internationally as one of the most representative of minimalist taste. The success of the brand is due to her insights and her collaborations. She was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Royal college of art in London in 2000 for continued experimentation with materials and original aesthetic innovation. In 2015 she was awarded the title of Knight Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic.
Teresa Sarti – Strada
Teresa Sarti, married Strada, born in Sesto San Giovanni in 1946, was an Italian philanthropist and Italian teacher, co-founder with her husband Gino Strada of the NGO Emergency in 1994, of which she was also the first president. The idea of creating a medical facility in war zones belongs to Teresa. Furthermore, she was convinced that it was necessary to start from the schools to create a new awareness and lay the foundations for a better world. In fact, she produced an ad hoc comic strip for the students, starring Lupo Alberto, much loved by children and adolescents. The motto is: above the war there are those who live, under the war there are those who die. She is classified among the thirteen women who made Italy.
Matilde Serao
Matilde Serao, born in Patras in 1856, was a writer and journalist. A true icon in the field of journalism, she was the first woman to have founded and directed a newspaper, Il Mattino. The Neapolitan world, so full of inspiration and contradictions, nourished his desire to write, tell and speak. For her, journalism was a field of observations, of customs, which she then recounted in her novels. Her notes on fashion, food, sport, worldly events, the novelties of progress, customs and traditions were counterbalanced by particular attention to social facts and events. She also published articles in the Giornale delle Donne “The Women’s Magazine”, one of the leading emancipationist magazines of the time.
Franca Viola
Franca Viola, born in Trapani in 1947, went down in history for being the first Italian woman to have refused a shotgun wedding. At just seventeen, she had the courage to raise her voice and refuse the shotgun wedding with the man who had raped her for eight days, managing to report him and getting him an 11-year sentence. At the time, article 544 of the penal code provided for the “shotgun wedding”. In fact, the law imputed her as a “shameless woman”. According to the moral condemnation of the time, the girl, no longer a virgin, had to marry her rapist to maintain the family honor, or else she would remain a spinster forever. Franca and her family pronounced a revolutionary “no”. For the first time in Italian history, a woman opposed the law of men and changed the course of justice in cases of abuse forever. If today sexual violence is a crime punishable by law in Italy, the credit goes to this proud and courageous young woman.
Monica Vitti
Monica Vitti, pseudonym of Maria Luisa Ceciarelli, born in Rome in 1931, was a very famous Italian actress in the world of Italian cinema. She began her film career in the 1950s in films by directors such as Michelangelo Antonioni, Federico Fellini and Mario Monicelli. She was often associated with Antonioni’s “Trilogy of Incommunicability”, in which she played the role of restless and dissatisfied women, in search of meaning in life. She is a style icon for her beauty and her fashion sense. Her characteristic husky voice and her innate comedic panache accompanied her for almost forty years of career. She has won numerous awards for her film career. She was also an animal rights activist.
Lina Wertmüller
Lina Wertmüller, born in Rome in 1928, was an Italian director, screenwriter and writer. She began her career collaborating with Federico Fellini as assistant director. She was the first woman ever to have received an Oscar nomination for best director for the film “Pasqualino Settebellezze” in the 1977 ceremony. Themes of her films are the vices and virtues of men and women, of all times. She mixed sex warfare and left-wing politics in provocative films she described as grotesque and genre-defying such as “Metalworker Mimì Wounded in Honor,” “Swept Away by an Unusual Fate in the Blue Sea of August,” and “Pasqualino Settebellezze.” , which established her as one of the most original directors of the 1970s. In 2020 she was awarded the Honorary Academy Award for Her Lifetime Achievement.